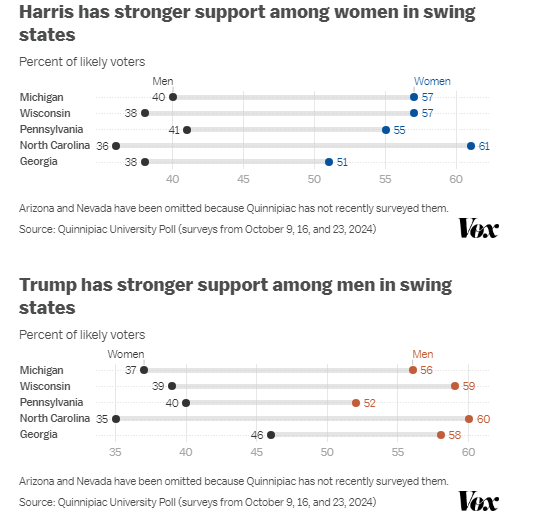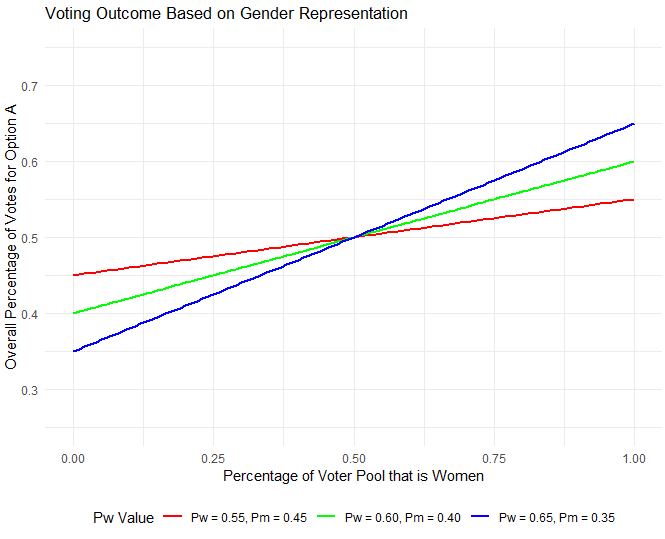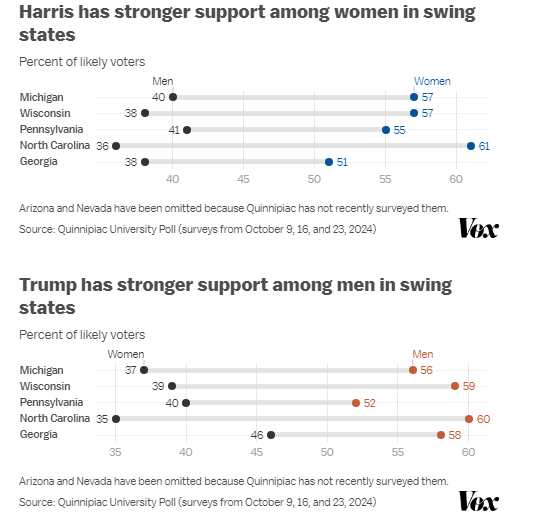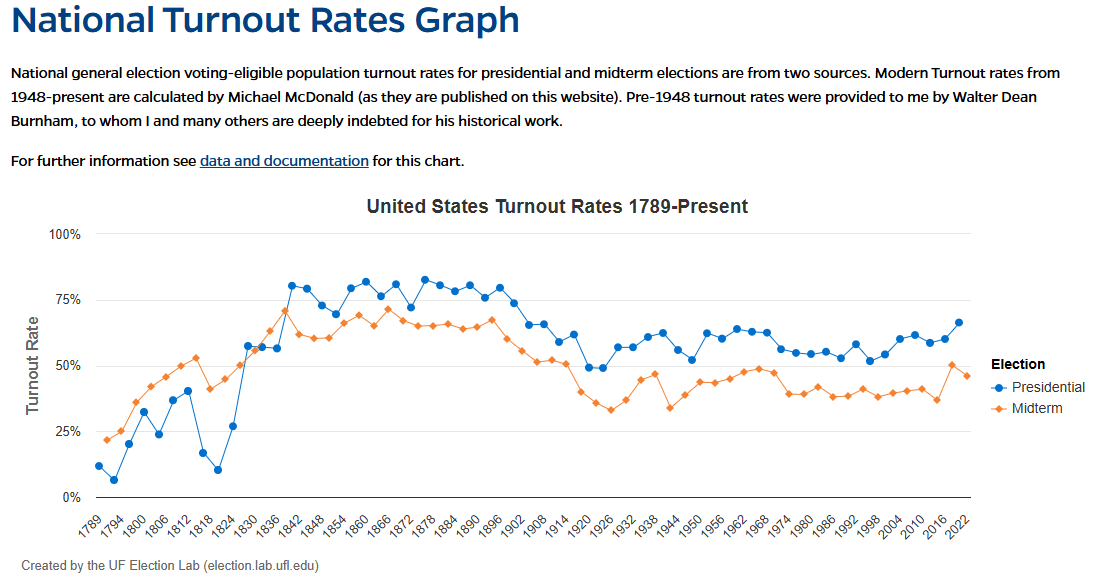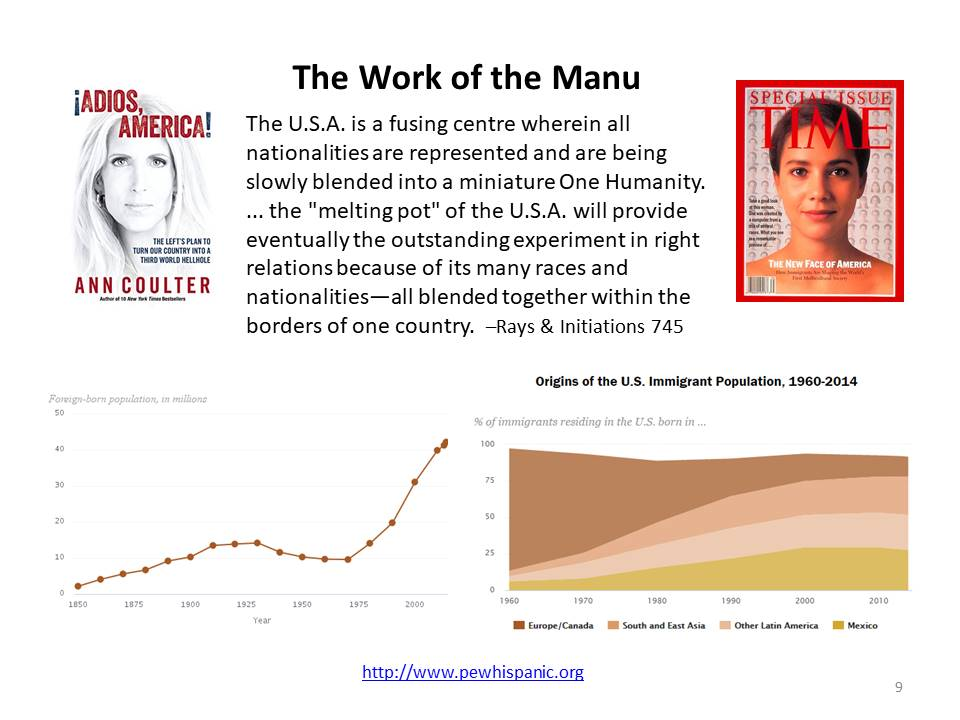
If a country rooted in transcendentalist values elects leaders who oppose these principles, it reflects a temporary misalignment between the nation’s deeper spiritual purpose (its “soul”) and its current political expression (its “personality”). This setback suggests that the country’s collective identity and values are still evolving, and there may be a need for growth and maturity before it can fully align its governance with its transcendental ideals. This process involves a journey toward greater self-awareness and authenticity, both at the individual and national levels, to eventually express its true spiritual purpose.
Transpersonal psychology
Transpersonal psychology is a distinctive branch of psychology that delves into experiences beyond the individual’s ego, focusing on spiritual and transcendent aspects of human existence. Unlike traditional psychology, which primarily centers on the individual’s mind and behavior, transpersonal psychology integrates spiritual dimensions and seeks to understand the broader spectrum of consciousness. It employs psychological methods to explore these transcendent experiences, emphasizing personal transformation and the evolution of consciousness. Transpersonal psychology aims to bridge the gap between psychology and spirituality, offering a holistic approach to understanding human potential.
Some notable figures in the field of transpersonal psychology are:
- Abraham Maslow: Known for his hierarchy of needs, Maslow is considered one of the founders of transpersonal psychology, particularly through his work on self-actualization and peak experiences.
- Ken Wilber: A philosopher and writer who has extensively contributed to transpersonal psychology through his integral theory, which seeks to integrate various dimensions of human experience.
- Carl Jung: Although not exclusively a transpersonal psychologist, Jung’s work on the collective unconscious and archetypes has significantly influenced the field.
- Roberto Assagioli: The founder of psychosynthesis, a therapeutic approach that incorporates spiritual development and personal growth, aligning closely with transpersonal psychology principles.
These individuals have played pivotal roles in shaping the understanding and development of transpersonal psychology, each contributing unique insights into the spiritual and transcendent aspects of human experience.
Transpersonal Politics
Incorporating transpersonal psychology into the political realm offers a compelling framework for understanding national dynamics through the lens of transpersonal sociology. By viewing a country as possessing both a soul (transpersonal self) and a personality (personal self), we can gain deeper insights into its collective identity and governance processes.
The concept of a nation’s soul represents its transcendent aspirations, core values, and ultimate purpose—an embodiment of collective consciousness striving for meaning and unity. Meanwhile, the personality of a nation reflects its tangible attributes, such as cultural characteristics, political structures, and socio-economic conditions. Together, they form the holistic identity of a country, akin to an individual’s spiritual and personal identity.
Periodic elections in a democracy serve as a critical mechanism to assess the alignment between a country’s soul and personality. These democratic processes can be seen as opportunities for introspection and evaluation, where the electorate reviews whether current political leaders and policies resonate with the nation’s deeper purpose. When the soul and personality are aligned, the country experiences harmony and progress, as the political body authentically represents the collective will and aspirations of its people. Conversely, misalignment may manifest as societal unrest, polarization, or stagnation, signaling a disconnect between governance and the populace’s core values.
This perspective can profoundly influence political strategies and policy-making. By integrating spiritual and psychological dimensions, leaders can craft policies that not only address immediate concerns but also nurture the nation’s soul. This holistic approach encourages policies that foster unity, sustainability, and long-term growth, aligning with deeper values rather than short-term gains.
Moreover, embracing this framework can redefine national identity, encouraging citizens to engage with politics not just as a civic duty but as a spiritual journey towards collective evolution. It invites a shift from adversarial politics to one of collaboration and shared purpose, where governance becomes a means of nurturing the soul of the nation.
Ultimately, the application of transpersonal psychology in politics through transpersonal sociology provides a transformative lens. It calls for a governance model that harmonizes the spiritual and practical aspects of national identity, fostering a more integrated and enlightened approach to leadership and citizenship.
American Transcendentalism
American Transcendentalism, particularly through the work of Ralph Waldo Emerson, can be seen as a profound expression of the soul of the United States. Emerson’s emphasis on individualism, self-reliance, and the inherent goodness of people and nature mirrors the spiritual and philosophical aspirations that have long defined the American ethos.
Emerson championed the idea that every individual possesses an innate connection to the divine, advocating for a direct relationship with nature and the universe. This belief in the fundamental goodness and potential of each person reflects the nation’s quest for freedom and personal growth. By promoting self-reliance, Emerson encouraged individuals to trust their intuition and inner voice, aligning with the American spirit of independence and innovation.
These transcendentalist ideals resonated deeply within the broader cultural and historical context of the United States. During a time of rapid expansion and change, Emerson’s work provided a philosophical framework that celebrated the individual’s role in shaping their destiny and the nation’s future. His vision of a society that values personal insight over conformity and materialism speaks to the enduring American pursuit of truth and authenticity.
Moreover, Emerson’s ideas highlighted the interconnectedness of humanity and nature, fostering a sense of unity that transcends societal divisions. This aspect of transcendentalism underscores the nation’s deeper values of equality and communal harmony, suggesting a collective soul that aspires to transcend personal and cultural boundaries.
Emerson’s transcendentalist ideals and Rousseau’s Social Contract share a profound philosophical kinship, particularly in their emphasis on individual freedom, self-reliance, and the inherent goodness of people. Both thinkers advocate for societies that respect individual rights and nurture personal development, envisioning environments where individuals can flourish alongside their natural rights. While Emerson and Rousseau were not contemporaries—Rousseau lived during the 18th century, whereas Emerson thrived in the 19th century—Rousseau’s ideas significantly influenced later transcendentalist thought. Their shared vision underscores the importance of a society where each person’s potential is realized in harmony with communal well-being.
In essence, Emerson’s transcendentalist ideals encapsulate the United States’ spiritual and philosophical core, embodying its enduring values and purpose. They offer a lens through which to understand the nation’s ongoing journey toward realizing its highest potential, both individually and collectively.
Some other notable figures in the Transcendentalist movement were:
- Henry David Thoreau: A close associate of Emerson, Thoreau is best known for his book “Walden,” which reflects on simple living in natural surroundings. His essay “Civil Disobedience” has also been influential, advocating for individual resistance to unjust government practices.
- Margaret Fuller: A pioneering feminist and writer, Fuller was an editor of the transcendentalist journal “The Dial.” Her work “Woman in the Nineteenth Century” is considered one of the earliest works of feminist philosophy in the United States.
- Bronson Alcott: An educator and reformer, Alcott was known for his innovative ideas on education and his role in founding the utopian community Fruitlands. He emphasized the importance of nurturing the spiritual and moral development of children.
- Louisa May Alcott: Although more famous for her novel “Little Women,” Louisa was influenced by transcendentalist ideas through her father, Bronson Alcott. Her writings often reflect themes of individualism and moral integrity.
- Walt Whitman: While not strictly a transcendentalist, Whitman’s poetry, especially in “Leaves of Grass,” embodies transcendentalist themes of nature, the self, and the interconnectedness of all life.
These figures, along with Emerson, contributed significantly to the development of transcendentalist thought, each bringing unique perspectives and insights that enriched the movement’s exploration of spirituality, individuality, and social reform.
Individual freedom, moral integrity, and truth-seeking
Transcendentalist philosophy, with its core principles of individualism, self-reliance, and inherent truth, stands in stark contrast to the ideals underpinning authoritarian domestic governments, international imperialism, and modern conspiracy theories that deny factual truths such as climate change.
- Authoritarian Domestic Governments: Transcendentalism fundamentally opposes authoritarianism, which often relies on the suppression of individual freedoms and a centralized control of power. At its heart, transcendentalism celebrates personal insight and the right to question authority, advocating for a society where individuals trust their intuition and moral compass. This emphasis on personal freedom and moral integrity directly challenges authoritarian structures that demand conformity and obedience, making these two philosophies largely incompatible.
- International Imperialism: The transcendentalist focus on self-reliance and the inherent value of all individuals contrasts sharply with the principles of imperialism, which involve the domination and exploitation of other nations for political and economic gain. Transcendentalism promotes the idea of respecting and nurturing the unique spirit of each community and culture. This philosophy inherently criticizes imperialistic practices that undermine sovereignty and impose external control, advocating instead for a harmonious coexistence rooted in mutual respect and understanding.
- Modern Conspiracy Theorists: Transcendentalists hold a deep commitment to truth and a reverence for nature, principles which conflict with the denial of scientific facts seen in some modern conspiracy theories. Transcendentalism encourages a direct and honest engagement with reality, celebrating the beauty and truths of the natural world. It values empirical evidence and rational thought, which are often dismissed by conspiracy theories that reject established scientific consensus. This philosophical commitment to understanding and accepting factual truths positions transcendentalism at odds with movements that propagate misinformation and deny critical issues like climate change.
In summary, transcendentalism’s advocacy for individual freedom, moral integrity, and truth-seeking creates a philosophical tension with authoritarianism, imperialism, and conspiracy theories. The transcendentalist vision of a society built on respect for the natural world and the individual’s spiritual journey is largely incompatible with these ideologies, highlighting the enduring relevance and challenge of transcendentalist thought in confronting modern societal issues.
Practical Approaches
To bring transcendentalist ideas into modern society, we can focus on several practical approaches:
- Community-Based Education: Develop educational programs that emphasize critical thinking, creativity, and personal growth. Encourage students to explore their passions and develop self-reliance by integrating experiential learning and nature-based projects into the curriculum. This approach nurtures individualism and a deeper connection with the environment.
- Sustainable Living Practices: Promote lifestyles that reduce environmental impact and emphasize self-sufficiency. Encourage urban gardening, local food sourcing, and renewable energy use. Communities can organize workshops on sustainable practices, fostering a culture of ecological responsibility and interconnectedness with nature.
- Nature Conservation Policies: Advocate for policies that protect natural environments and biodiversity. Support initiatives that preserve green spaces and promote reforestation. Engage in community clean-up events and conservation projects, reinforcing the transcendentalist respect for nature.
- Personal Reflection and Mindfulness: Encourage practices such as meditation, journaling, and time spent in nature to cultivate self-awareness and inner peace. These activities align with transcendentalist values of introspection and spiritual growth, helping individuals connect with their true selves.
- Community Initiatives: Build local groups focused on transcendentalist values, such as book clubs, discussion forums, or volunteer organizations. These initiatives can provide spaces for sharing ideas, supporting each other’s personal journeys, and collectively engaging in projects that embody transcendentalist principles.
- Technology for Good: Use technology to spread transcendentalist ideas and connect like-minded individuals. Create online platforms for sharing resources, organizing events, and discussing topics related to individualism, self-reliance, and environmental stewardship while ensuring technology remains a tool for enhancing, not replacing, genuine human connections.
- Countering disinformation. To effectively use technology to spread transcendentalist ideas, it’s crucial to address the challenge of disinformation, particularly AI-enhanced disinformation. This requires a concerted effort to foster digital literacy and critical thinking skills, enabling individuals to discern credible information from misleading content. Implementing community guidelines and integrating fact-checking tools can help maintain the integrity of the information shared, ensuring that technology remains a tool for enhancing authentic human connections. By safeguarding the truth and promoting informed dialogue, these platforms can uphold and spread transcendentalist values effectively.
By integrating these strategies into daily life, individuals and communities can embody transcendentalist ideals, fostering a society that values personal freedom, ecological harmony, and spiritual fulfillment.
Governance influenced by transcendentalist principles
Throughout history, there have been notable instances where governance has been influenced by transcendentalist principles, often characterized by an emphasis on individualism, self-reliance, and a profound connection with nature.
- Brook Farm (1841-1847): Brook Farm was a utopian community in Massachusetts, founded by transcendentalists including George Ripley. The community aimed to integrate intellectual and manual labor, embodying ideals of self-reliance and collective harmony. While it faced practical challenges and eventually dissolved, Brook Farm remains a significant experiment in applying transcendentalist principles to governance and social organization.
- The Fruitlands Community (1843-1844): Founded by Bronson Alcott and Charles Lane, Fruitlands was another attempt at a transcendentalist utopia. It emphasized simple living, vegetarianism, and self-sufficiency, deeply rooted in a spiritual connection with nature. Despite its short existence, Fruitlands encapsulated the difficulties of aligning idealistic principles with practical governance.
- Henry David Thoreau’s Civil Disobedience (1849): While not a governance structure, Thoreau’s essay “Civil Disobedience” has inspired leaders and movements worldwide. Advocating for nonviolent resistance to unjust laws, it reflects transcendentalist values of personal integrity and moral action. This work influenced figures like Mahatma Gandhi and Martin Luther King Jr., highlighting its impact on governance and civil rights movements.
These examples illustrate the challenges of integrating transcendentalist philosophy with governance, often requiring a balance between idealism and practicality. While some efforts were short-lived, they contributed to a broader understanding of how transcendentalist principles can inspire societal change and influence policies aimed at individual and communal well-being.
The beloved community
Martin Luther King Jr.’s vision of the “beloved community” resonates deeply with transcendentalist philosophy, particularly its emphasis on individual dignity, moral integrity, and the interconnectedness of all people. King’s beloved community is a global vision in which all people can share in the wealth of the earth, marked by justice, equality, and love transcending race or social status. This concept reflects transcendentalist ideals by advocating for a society where individuals are valued for their unique contributions and where moral integrity guides social interactions.
In practical terms, implementing the beloved community involves initiatives that promote nonviolence, community building, and social justice. Nonviolent resistance, a cornerstone of King’s philosophy, aligns with transcendentalist values by championing moral integrity and personal courage. This approach encourages individuals to stand against injustice through peaceful means, fostering an environment where dialogue and understanding pave the way for reconciliation and change.
Community building is another critical element, where initiatives focus on creating inclusive spaces that reflect the interconnectedness and mutual respect advocated by transcendentalists. Programs that support cross-cultural dialogue, collaborative problem-solving, and community service can strengthen bonds among diverse groups, echoing King’s vision of a society united by common values.
Social justice initiatives are also vital, addressing systemic inequalities and advocating for policies that ensure equal opportunities for all individuals. This aligns with transcendentalist principles by promoting fairness and compassion, advocating for the inherent worth of every person.
King’s civil rights movement exemplifies the transcendentalist emphasis on both personal and collective transformation. By inspiring individuals to reflect on their own values and take action towards societal change, King embodied the transcendentalist belief that true progress begins within the individual and radiates outward to effect broader social transformation.
In creating the beloved community, transcendentalist philosophy finds a powerful expression through King’s work, offering a timeless blueprint for building a society rooted in justice, equality, and love.


Further readings: